
In the process, the product adsorb the VOCs onto a continuously rotating Zeolite rotor. The rotor is segregated into 3 parts - adsorption zone, cooling zone, and desorption zone. The VOC laden air passes through the adsorption sector of the rotor where the VOC's are removed from the process stream and adsorbed onto the Zeolite rotor. The process exhaust exits the adsorbent section without most of the VOC and is exhausted to the atmosphere.
Adsorption/process zone: The exhaust air from the process room having low concentration VOC and high volumes, is passed through rotating Zeolite rotor. The zeolite rotor adsorbs the VOCs and other pollutants in the adsorption/process zone.
Cooling zone: As we know, the desiccant performs better when cooler. The rotor is cooled down in the cooling zone in order to maintain the adsorption capacity and in the process heat is recover to save regeneration energy.
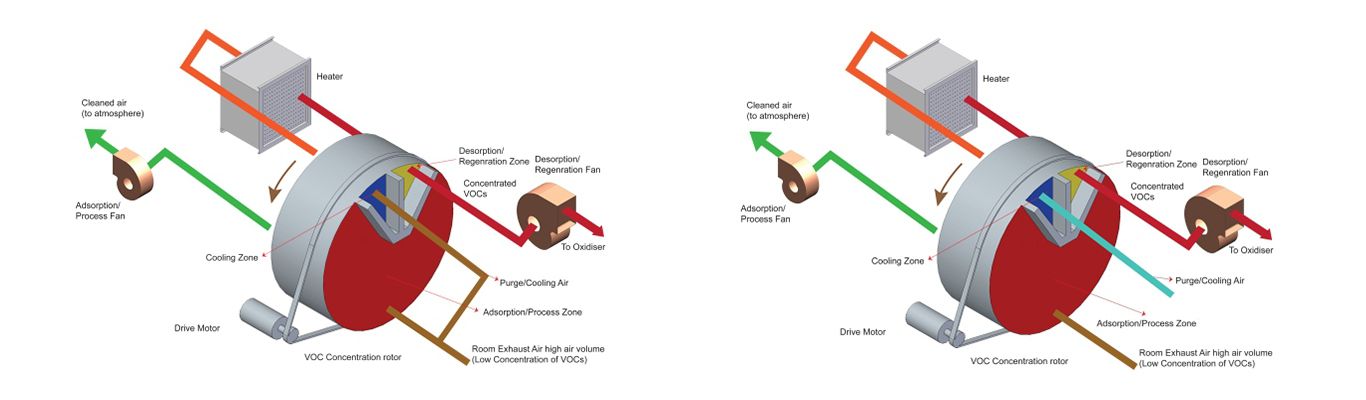
Desorption/Regeneration zone: The rotor is regenerated on a continuous basis as it moves from adsorption to desorption zone. The VOCs are desorbed by hot air (180-200 Deg C) and in the process, the leaving air is concentrated with VOCs. The concentration ratio can as high as 30 times. Generally, the concentration ratio is around 10-25 times.